Cytosine has one other interesting property that none of the other nucleotides have is that very often in the cell cytosine can have an extra chemical attached to them a methyl group.
Cytosine with a vinyl group.
Cytosine also known as c belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyrimidones.
Draw cytosine and show the methyl group on the molecule.
Pyrimidones are compounds that contain a pyrimidine ring which bears a ketone.
Cytosine definition a pyrimidine base c4h5n3o that is one of the fundamental components of dna and rna in which it forms a base pair with guanine.
Explore our library of.
It is a pyrimidine derivative with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached an amine group at position 4 and a keto group at position 2.
Create an account like this lesson share.
The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine in watson crick base.
Cytosine c5 dna mtases catalyze the transfer of the methyl group from a cofactor molecule s adenosyl l methionine adomet to the c5 position of cytosine residues in dna figure 1 in this reaction the 5 methylcytosine is created and the s adenosyl.
C is one of the four main bases found in dna and rna along with adenine guanine and thymine uracil in rna.
In such a conformation the amino group of the cytosine base is no longer in close proximity with the vinyl group of the original avp without the linker.
Cytosine exists as a solid soluble in water and a very weakly acidic compound based on its pka.
Pyrimidine is a 6 membered ring consisting of four carbon atoms and two nitrogen centers at the 1 and 3 ring positions.
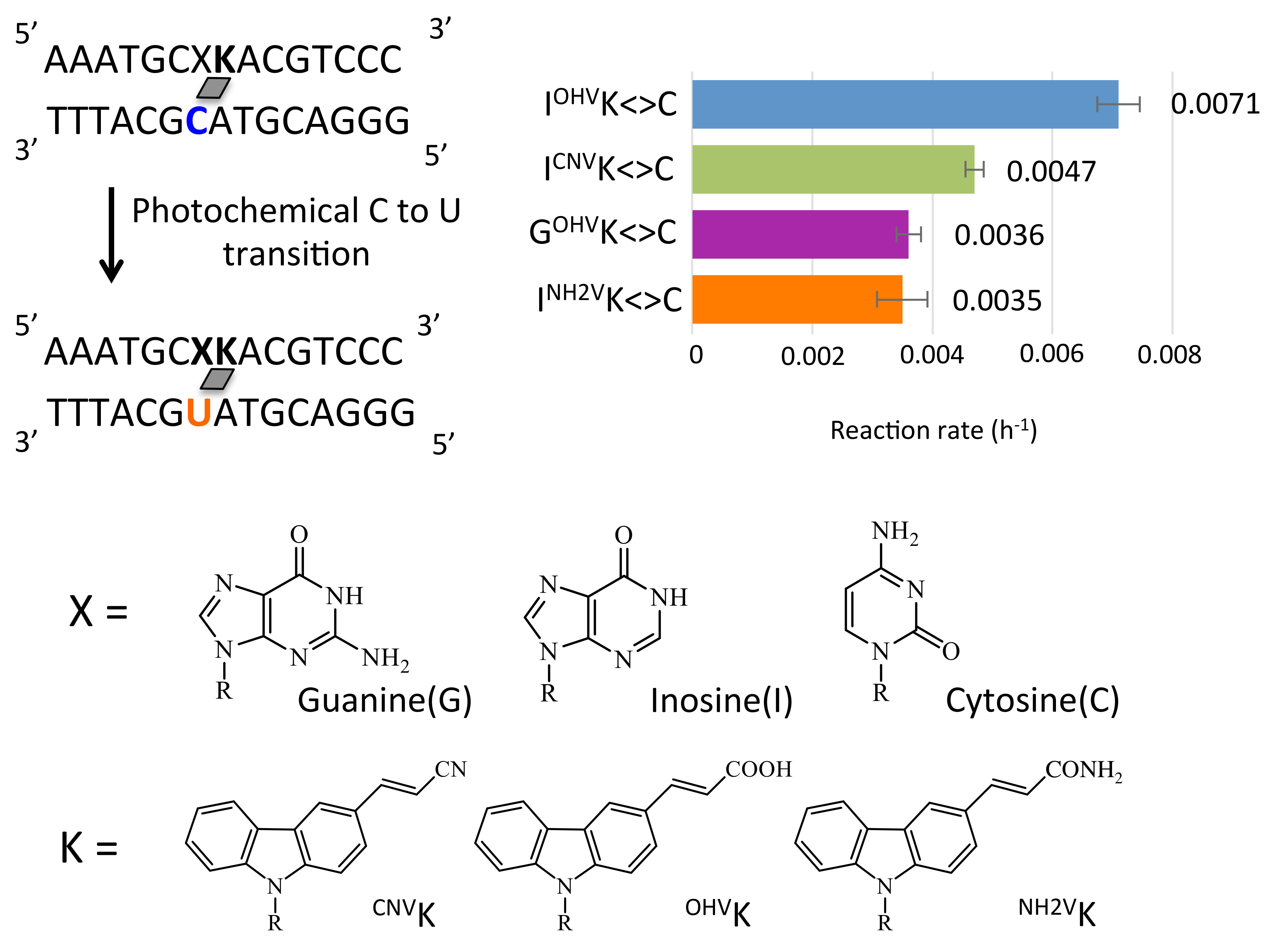
It was demonstrated that the e pyridinyl vinyl keto group was efficiently and specifically transferred to the 4 amino group of the opposing cytosine in rna in the presence of nicl 2 with more than 200 fold accelerated rate compared with the previous system with the use of the diketo transfer group.
Create an account to start this course today try it risk free for 30 days.
Jeltsch in reference module in biomedical sciences 2014.
Cytosine is one of several types of bases that are incorporated into the nucleic acid molecule nucleic acids are composed of a five carbon sugar bound to a phosphoric acid along with a nitrogenous base deoxyribonucleic acid the hereditary material of most living organisms consists of the five carbon sugar deoxyribose with a phosphate linkage to which is attached cytosine or any of three.
Cytosine ˈ s aɪ t ə ˌ s iː n ˌ z iː n ˌ s ɪ n.
The invention discloses a synthesis method of cytosine.
Base flipping and general catalytic mechanism of cytosine c5 mtases.
7 b1 vs.